The Truth Regarding Over-Pronation
One of the most common causes of foot and leg discomfort is a condition known as overpronation. Normal pronation, or "turning inward" of the foot is necessary as the foot adapts to the ground. With over pronation, the arch flattens, collapses, and soft tissues stretch. This causes the joint surfaces to function at unnatural angles to each other. When this happens, joints that should be stable now become very loose and flexible. At first, over pronation may cause fatigue. As the problem gets worse, strain on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the foot and lower leg can cause permanent problems and deformities.
Causes
Over-pronation is very prominent in people who have flexible, flat feet. The framework of the foot begins to collapse, causing the foot to flatten and adding stress to other parts of the foot. As a result, over-pronation, often leads to Plantar Fasciitis, Heel Spurs, Metatarsalgia, Post-tib Tendonitis and/or Bunions. There are many causes of flat feet. Obesity, pregnancy or repetitive pounding on a hard surface can weaken the arch leading to over-pronation. Often people with flat feet do not experience discomfort immediately, and some never suffer from any discomfort at all. However, when symptoms develop and become painful, walking becomes awkward and causes increased strain on the feet and calves.
Symptoms
Common conditions that develop with prolonged overpronation typically include plantar fasciitis, achilles tendonitis, shin splints, posterior tibial stress syndrome and even IT band syndrome. With long term neglect you may see the development of bunyons, foot deformities and early onset of hip and knee arthritis.
Diagnosis
The best way to discover whether you have a normal gait, or if you overpronate, is to visit a specialty run shop, an exercise physiologist, a podiatrist or a physical therapist who specializes in working with athletes. A professional can analyze your gait, by watching you either walk or run, preferably on a treadmill. Some facilities can videotape your gait, then analyze the movement of your feet in slow-motion. Another (and less costly) way is to look at the bottom of an older pair of run shoes. Check the wear pattern. A person with a normal gait will generally see wear evenly across the heel and front of the shoe. A person who overpronates will likely see more wear on the OUTside of the heel and more wear on the INside of the forefoot (at the ball). A person who supinates will see wear all along the outer edges of the shoe. You can also learn about your gait by looking at your arches. Look at the shape your wet feet leave on a piece of paper or a flat walking surface.

Non Surgical Treatment
The way a foot orthotic works is by altering the weight-bearing surface of the foot. The simulated foot improvement is only possible when standing still with full weight applied. Orthotics are of little help through most of the actual walking cycle. observationPatients may experience some symptom relief, but the orthotic cannot correct the internal osseous misalignment. Over-the-counter foot orthotics are usually of little help and wear out quickly. Custom-made foot orthotics, obtained through your doctor's office, are generally expensive. Though they last longer and have less chance of ill-effects than OTC brands, they still need to be replaced often. Over a lifetime, an individual can spend several thousands of dollars in total costs associated with orthotics and see little or no results. This is because orthotics only work when you are wearing them and do not treat the cause of the problem. In many cases, the external pressure points created by orthotics can cause more problems than solutions. Blisters, sore feet, sore joints and many other long-term complications can arise as a consequence of wearing orthotics.
Prevention
Duck stance: Stand with your heels together and feet turned out. Tighten the buttock muscles, slightly tilt your pelvis forwards and try to rotate your legs outwards. You should feel your arches rising while you do this exercise.
Calf stretch:Stand facing a wall and place hands on it for support. Lean forwards until stretch is felt in the calves. Hold for 30 seconds. Bend at knees and hold for a further 30 seconds. Repeat 5 times.
Golf ball:While drawing your toes upwards towards your shins, roll a golf ball under the foot between 30 and 60 seconds. If you find a painful point, keep rolling the ball on that spot for 10 seconds.
Big toe push: Stand with your ankles in a neutral position (without rolling the foot inwards). Push down with your big toe but do not let the ankle roll inwards or the arch collapse. Hold for 5 seconds. Repeat 10 times. Build up to longer times and fewer repetitions.
Ankle strengthener: Place a ball between your foot and a wall. Sitting down and keeping your toes pointed upwards, press the outside of the foot against the ball, as though pushing it into the wall. Hold for 5 seconds and repeat 10 times.
Arch strengthener: Stand on one foot on the floor. The movements needed to remain balanced will strengthen the arch. When you are able to balance for 30 seconds, start doing this exercise using a wobble board.
What Exactly Is Severs Disease?
Severs? disease usually presents with pain in either one or both of a sufferer?s heels. The area can be sore or tender, particularly first thing in the morning or after squeezing. Because the pain is focussed on the heel, an important part of the foot that makes contact with the ground through virtually all movement, sufferers often have to limp to alleviate their discomfort. The pain of Severs? disease is at its worst after any exertion that involves contact between a heel and the ground, particularly strenuous exercise like running or sport. The condition is caused by the wear and tear of structures in the heel, most significantly the heel bone and any attached tendons. Severs? disease is prevalent in young children who are extremely active, particularly as the heel and its attached tendons are still growing in the age group the condition most commonly affects (7-14).
Causes
At birth, most of our foot bones are still made of cartilage, which ossifies (becomes bony) over the first few years of life. At the back of the heel, there is a growth plate that is attached to the main body of the heel bone by a cartilaginous join. At about the age of 14-15 years, this area of cartilage between the growth plate and the heel bone ossifies, fusing the area to the heel. Sever?s disease occurs when there is too much motion or strain across the growth plate, resulting in this area becoming inflamed and painful.
Symptoms
The patient complains of activity related pain that usually settles with rest. On Examination the heel bone - or calcaneum - is tender on one or both sides. The gastrocnemius and soleus muscles (calf muscles) may be tight and bending of the ankle might be limited because of that. Foot pronation (rolling in) often exacerbates the problem. There is rarely anything to see and with no redness or swelling and a pain that comes and goes mum and dad often wait before seeking advice on this condition. The pain may come on partway through a game and get worse or come at the end of the game. Initially pain will be related only to activity but as it gets worse the soreness will still be there the next morning and the child might limp on first getting up.
Diagnosis
A doctor or other health professional such as a physiotherapist can diagnose Sever?s disease by asking the young person to describe their symptoms and by conducting a physical examination. In some instances, an x-ray may be necessary to rule out other causes of heel pain, such as heel fractures. Sever?s disease does not show on an x-ray because the damage is in the cartilage.
Non Surgical Treatment
Cold packs: Apply ice or cold packs to the back of the heels for around 15 minutes after any physical activity, including walking.
Shoe inserts: Small heel inserts worn inside the shoes can take some of the traction pressure off the Achilles tendons. This will only be required in the short term.
Medication: Pain-relieving medication may help in extreme cases, but should always be combined with other treatment and following consultation with your doctor).
Anti-inflammatory creams: Also an effective management tool.
Splinting or casting: In severe cases, it may be necessary to immobilise the lower leg using a splint or cast, but this is rare.
Time: Generally the pain will ease in one to two weeks, although there may be flare-ups from time to time.
Correction of any biomechanical issues: A physiotherapist can identify and discuss any biomechanical issues that may cause or worsen the condition.
Education: Education on how to self-manage the symptoms and flare-ups of Sever?s disease is an essential part of the treatment.
Surgical Treatment
The surgeon may select one or more of the following options to treat calcaneal apophysitis. Reduce activity. The child needs to reduce or stop any activity that causes pain. Support the heel. Temporary shoe inserts or custom orthotic devices may provide support for the heel. Medications. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, help reduce the pain and inflammation. Physical therapy. Stretching or physical therapy modalities are sometimes used to promote healing of the inflamed issue. Immobilization. In some severe cases of pediatric heel pain, a cast may be used to promote healing while keeping the foot and ankle totally immobile. Often heel pain in children returns after it has been treated because the heel bone is still growing. Recurrence of heel pain may be a sign of calcaneal apophysitis, or it may indicate a different problem. If your child has a repeat bout of heel pain, be sure to make an appointment with your foot and ankle surgeon.
The Treatments And Causes
Overview
Adult flatfoot refers to a deformity that develops after skeletal maturity is reached. Adult flatfoot should be differentiated from constitutional flatfoot, which is a common congenital non-pathologic foot morphology. There are numerous causes of acquired adult flatfoot, including fracture or dislocation, tendon laceration, tarsal coalition, arthritis, neuroarthropathy, neurologic weakness, and iatrogenic causes. 
Causes
As discussed above, many different problems can create a painful flatfoot. Damage to the posterior tibial tendon is the most common cause of AAFD. The posterior tibial tendon is one of the most important tendons of the leg. It starts at a muscle in the calf, travels down the inside of the lower leg and attaches to the bones on the inside of the foot. The main function of this tendon is to support the arch of your foot when you walk. If the tendon becomes inflamed or torn, the arch will slowly collapse. Women and people over 40 are more likely to develop problems with the posterior tibial tendon. Other risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and hypertension. Having flat feet since childhood increases the risk of developing a tear in the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, people who are involved in high impact sports, such as basketball, tennis, or soccer, may have tears of the tendon from repetitive use. Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause a painful flatfoot. This type of arthritis attacks not only the cartilage in the joints, but also the ligaments that support the foot. Inflammatory arthritis not only causes pain, but also causes the foot to change shape and become flat. The arthritis can affect the back of the foot or the middle of foot, both of which can result in a fallen arch. An injury to the tendons or ligaments in the foot can cause the joints to fall out of alignment. The ligaments support the bones and prevent them from moving. If the ligaments are torn, the foot will become flat and painful. This more commonly occurs in the middle of the foot (Lisfranc injury), but can also occur in the back of the foot. Injuries to tendons of the foot can occur either in one instance (traumatically) or with repeated use over time (overuse injury). Regardless of the cause, if tendon function is altered, the forces that are transmitted across joints in the foot are changed and this can lead to increased stress on joint cartilage and ligaments. In addition to tendon and ligament injuries, fractures and dislocations of the bones in the midfoot can also lead to a flatfoot deformity. People with diabetes or with nerve problems that limits normal feeling in the feet, can have collapse of the arch or of the entire foot. This type of arch collapse is typically more severe than that seen in patients with normal feeling in their feet. In addition to the ligaments not holding the bones in place, the bones themselves can sometimes fracture and disintegrate without the patient feeling any pain. This may result in a severely deformed foot that is very challenging to correct with surgery. Special shoes or braces are the best method for dealing with this problem.
Symptoms
Patients will usually describe their initial symptoms as "ankle pain", as the PT Tendon becomes painful around the inside of the ankle joint. The pain will become more intense as the foot flattens out, due to the continued stretching and tearing of the PT Tendon. As the arches continue to fall, and pronation increases, the heel bone (Calcaneus) tilts into a position where it pinches against the ankle bone (Fibula), causing pain on both the inside and outside of the ankle. As the foot spends increased time in a flattened, or deformed position, Arthritis can begin to affect the joints of the foot, causing additional pain.
Diagnosis
Starting from the knee down, check for any bowing of the tibia. A tibial varum will cause increased medial stress on the foot and ankle. This is essential to consider in surgical planning. Check the gastrocnemius muscle and Achilles complex via a straight and bent knee check for equinus. If the range of motion improves to at least neutral with bent knee testing of the Achilles complex, one may consider a gastrocnemius recession. If the Achilles complex is still tight with bent knee testing, an Achilles lengthening may be necessary. Check the posterior tibial muscle along its entire course. Palpate the muscle and observe the tendon for strength with a plantarflexion and inversion stress test. Check the flexor muscles for strength in order to see if an adequate transfer tendon is available. Check the anterior tibial tendon for size and strength.
Non surgical Treatment
Depending on the stage of the deformity and patient?s functional goals, various treatment options are available. Some patients improve with conservative care which includes rest and immobilization, shoe modifications, orthoses and bracing, or physical therapy. Surgery might be warranted for advanced stages of the condition. Often a combination of procedures including tendon and muscle augmentation, tendon transfers, realigning of bones or fusion of certain joints might be necessary in more advanced cases. Your doctor will evaluate and recommend an individualized plan of care with your specific needs in mind. 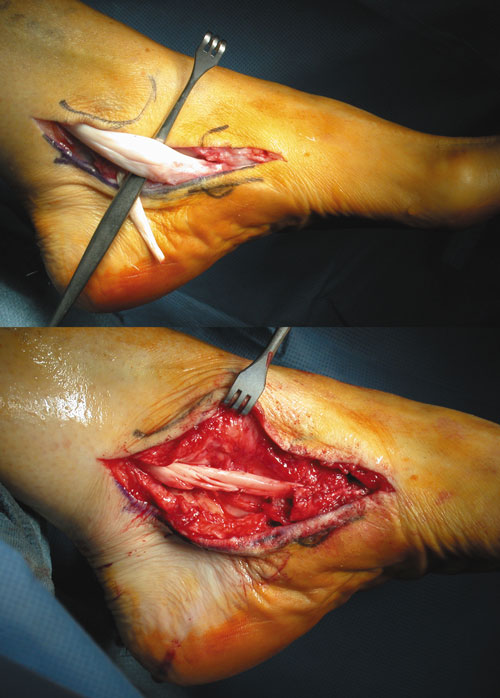
Surgical Treatment
In cases of PTTD that have progressed substantially or have failed to improve with non-surgical treatment, surgery may be required. For some advanced cases, surgery may be the only option. Surgical treatment may include repairing the tendon, tendon transfers, realigning the bones of the foot, joint fusions, or both. Dr. Piccarelli will determine the best approach for your specific case. A variety of surgical techniques is available to correct flexible flatfoot. Your case may require one procedure or a combination of procedures. All of these surgical techniques are aimed at relieving the symptoms and improving foot function. Among these procedures are tendon transfers or tendon lengthening procedures, realignment of one or more bones, or insertion of implant devices. Whether you have flexible flatfoot or PTTD, to select the procedure or combination of procedures for your particular case, Dr. Piccarelli will take into consideration the extent of your deformity based on the x-ray findings, your age, your activity level, and other factors. The length of the recovery period will vary, depending on the procedure or procedures performed.
What Causes Heel Pain

Heel Pain is one of the most common conditions treated by podiatrists. It is often a message that something is in need of medical attention. Pain that occurs right after an injury or early in an illness may play a protective role, often warning us about the damage we have suffered. Heel pain is a problem which affects people of all ages and vocations, whether they are active or not and it comes in many different forms. Heel pain can also occur in children usually between the ages of 8 and 13, as they become increasingly active in sporting activities and during the growing phase.
Causes
There are several causes of heel pain. By far the most common cause in adults is a condition commonly known as plantar fasciitis. Other names occasionally used for the same condition are heel spurs, and policeman?s heel. Plantar means bottom of the foot, and fascia is the fibrous tissues that helps tether the heel bone (calcaneus) to the heads of the metatarsal bones found at the base of your toes The meaning of ?itis? is inflammation. However, inflammation does not have a large part to play in the pathology, it is more degenerative (wear & tear) so the preferred title is plantar fasciosis or plantar aponeurotic fasciosis. For simplicity sake, we will refer to this common cause of heel pain as plantar fasciitis in this manual.
Symptoms
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are classically pain of a sharp nature which is worse standing first thing in the morning. After a short period of walking the pain usually reduces or disappears, only to return again later in the day. Aggravating times are often after increased activity and rising from sitting. If these are the sort of symptoms you are experiencing then the Heel-Fix Kit ? will be just the treatment your heel is crying out for. Some heel pain is more noticeable at night and at rest. Because plantar fasciitis is a mechanical pathology it is unlikely that this sort of heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis. The most common reason for night heel pain is pressure on your Sciatic nerve causing referred pain in the heel. Back pain is often present as well, but you can get the heel pain with little or no back pain that is caused by nerve irritation in the leg or back. If you get pain in your heels mainly or worse at night please see a clinician as soon as you can to confirm the diagnosis.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist (doctor who specializes in the evaluation and treatment of foot diseases) will carry out a physical examination, and ask pertinent questions about the pain. The doctor will also ask the patient how much walking and standing the patient does, what type of footwear is worn, and details of the his/her medical history. Often this is enough to make a diagnosis. Sometimes further diagnostic tests are needed, such as blood tests and imaging scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
Home care, in cases that are not severe, home care is probably enough to get rid of heel pain. Rest, avoid running or standing for long periods, or walking on hard surfaces. Avoid activities that may stress the heels. Ice, place an ice-pack on the affected area for about 15 minutes. Do not place bare ice directly onto skin. Footwear. proper-fitting shoes that provide good support are crucial. Athletes should be particularly fussy about the shoes they use when practicing or competing - sports shoes need to be replaced at specific intervals (ask your trainer). Foot supports, wedges and heel cups can help relieve symptoms.
Surgical Treatment
When a diagnosis of plantar fasciitis is made early, most patients respond to conservative treatment and don?t require surgical intervention. Often, when there is a secondary diagnosis contributing to your pain, such as an entrapped nerve, and you are non-responsive to conservative care, surgery may be considered. Dr. Talarico will discuss all options and which approach would be the most beneficial for your condition.
Prevention

Maintaining flexible and strong muscles in your calves, ankles, and feet can help prevent some types of heel pain. Always stretch and warm-up before exercising. Wear comfortable, properly fitting shoes with good arch support and cushioning. Make sure there is enough room for your toes.
Living With Achilles Tendinitis
 Achilles tendinitis (tendonitis) or Achilles tendon inflammation occurs when the Achilles tendon becomes inflamed, as a result, of the Achilles tendon being put under too much strain. The Achilles tendon joins the calf muscles to the heel bone, and is found at the back of a person's lower leg. It is the largest tendon in the body and can endure great force, but is still susceptible to injury. Achilles tendinitis is usually the result of strenuous, high impact exercise, such as running. If ignored, Achilles tendinitis can lead to the tendon tearing or rupturing, and therefore it is important to seek the necessary treatment. Sometimes, treatment can be as simple as getting rest or changing an exercise routine. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be required.
Achilles tendinitis (tendonitis) or Achilles tendon inflammation occurs when the Achilles tendon becomes inflamed, as a result, of the Achilles tendon being put under too much strain. The Achilles tendon joins the calf muscles to the heel bone, and is found at the back of a person's lower leg. It is the largest tendon in the body and can endure great force, but is still susceptible to injury. Achilles tendinitis is usually the result of strenuous, high impact exercise, such as running. If ignored, Achilles tendinitis can lead to the tendon tearing or rupturing, and therefore it is important to seek the necessary treatment. Sometimes, treatment can be as simple as getting rest or changing an exercise routine. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be required.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis most commonly occurs due to repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on the Achilles tendon. This typically occurs due to excessive walking, running or jumping activities. Occasionally, it may occur suddenly due to a high force going through the Achilles tendon beyond what it can withstand. This may be due to a sudden acceleration or forceful jump. The condition may also occur following a calf or Achilles tear, following a poorly rehabilitated sprained ankle or in patients with poor foot biomechanics or inappropriate footwear. In athletes, this condition is commonly seen in running sports such as marathon, triathlon, football and athletics.
Symptoms
Mild ache in the back of the lower leg, especially after running. More acute pain may occur after prolonged activity, Tenderness or stiffness in the morning. In most cases the pain associated with Achilles tendinitis is more annoying than debilitating, making sufferers regret activity after the fact, but not keeping them from doing it. More severe pain around the Achilles tendon may be a symptom of a much more serious ruptured tendon.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Supportive shoes and orthotics. Pain from insertional Achilles tendinitis is often helped by certain shoes, as well as orthotic devices. For example, shoes that are softer at the back of the heel can reduce irritation of the tendon. In addition, heel lifts can take some strain off the tendon. Heel lifts are also very helpful for patients with insertional tendinitis because they can move the heel away from the back of the shoe, where rubbing can occur. They also take some strain off the tendon. Like a heel lift, a silicone Achilles sleeve can reduce irritation from the back of a shoe. If your pain is severe, your doctor may recommend a walking boot for a short time. This gives the tendon a chance to rest before any therapy is begun. Extended use of a boot is discouraged, though, because it can weaken your calf muscle. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT). During this procedure, high-energy shockwave impulses stimulate the healing process in damaged tendon tissue. ESWT has not shown consistent results and, therefore, is not commonly performed. ESWT is noninvasive-it does not require a surgical incision. Because of the minimal risk involved, ESWT is sometimes tried before surgery is considered.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be considered to relieve Achilles tendinitis only if the pain does not improve after 6 months of nonsurgical treatment. The specific type of surgery depends on the location of the tendinitis and the amount of damage to the tendon. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the Achilles tendon, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite consistent stretching. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope-an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Gastrocnemius recession can be performed with or without d?bridement, which is removal of damaged tissue. D?bridement and repair (tendon has less than 50% damage). The goal of this operation is to remove the damaged part of the Achilles tendon. Once the unhealthy portion of the tendon has been removed, the remaining tendon is repaired with sutures, or stitches to complete the repair. In insertional tendinitis, the bone spur is also removed. Repair of the tendon in these instances may require the use of metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon to the heel bone, where it attaches. After d?bridement and repair, most patients are allowed to walk in a removable boot or cast within 2 weeks, although this period depends upon the amount of damage to the tendon. D?bridement with tendon transfer (tendon has greater than 50% damage). In cases where more than 50% of the Achilles tendon is not healthy and requires removal, the remaining portion of the tendon is not strong enough to function alone. To prevent the remaining tendon from rupturing with activity, an Achilles tendon transfer is performed. The tendon that helps the big toe point down is moved to the heel bone to add strength to the damaged tendon. Although this sounds severe, the big toe will still be able to move, and most patients will not notice a change in the way they walk or run. Depending on the extent of damage to the tendon, some patients may not be able to return to competitive sports or running. Recovery. Most patients have good results from surgery. The main factor in surgical recovery is the amount of damage to the tendon. The greater the amount of tendon involved, the longer the recovery period, and the less likely a patient will be able to return to sports activity. Physical therapy is an important part of recovery. Many patients require 12 months of rehabilitation before they are pain-free.
Prevention
Stay in good shape year-round and try to keep your muscles as strong as they can be. Strong, flexible muscles work more efficiently and put less stress on your tendon. Increase the intensity and length of your exercise sessions gradually. This is especially important if you've been inactive for a while or you're new to a sport. Always warm up before you go for a run or play a sport. If your muscles are tight, your Achilles tendons have to work harder to compensate. Stretch it out. Stretch your legs, especially your calves, hamstrings, quadriceps, and thigh muscles - these muscles help stabilize your knee while running. Get shoes that fit properly and are designed for your sport. If you're a jogger, go to a running specialty store and have a trained professional help you select shoes that match your foot type and offer plenty of support. Replace your shoes before they become worn out. Try to run on softer surfaces like grass, dirt trails, or synthetic tracks. Hard surfaces like concrete or asphalt can put extra pressure on the joints. Also avoid running up or down hills as much as possible. Vary your exercise routine. Work different muscle groups to keep yourself in good overall shape and keep individual muscles from getting overused. If you notice any symptoms of Achilles tendonitis, stop running or doing activities that put stress on your feet. Wait until all the pain is gone or you have been cleared to start participating again by a doctor.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis And Simple Methods To Prevent It
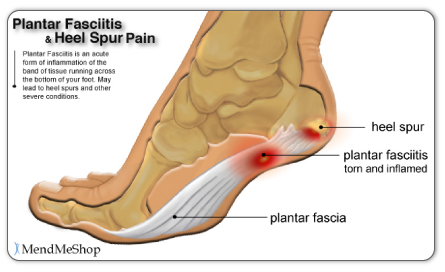
Overview
The plantar fascia is a strong, relatively inflexible, fibrous ligament band that runs through the bottom of the foot. That band helps to keep the complex arch system of the foot, absorb shock, plays a role in body balance and in the various phases of gait. The band transmits your weight across the bottom of the foot with each step you take. When the heel of the trailing leg starts to get off the ground, the band bears tension that is approximately twice the body weight. The tension on the band at this moment is even greater if the calf muscles are not flexible enough.
Causes
It usually starts following an increase in activity levels. Increase in weight. Standing for long periods. Poor footwear. Tight muscle groups. Abnormal pressure on the plantar Fascia can be caused by any of the above. The plantar fascia becomes inflamed and tiny rips can occur where it attaches into the inside of the heel bone. The area becomes inflamed and swollen, and it is the increase in fluid to the area that accumulates when weight is taken off the area that then causes the pain on standing.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis commonly causes a stabbing pain in the heel of the foot, which is worse during the first few steps of the day after awakening. As you continue to walk on the affected foot, the pain gradually lessens. Usually, only one foot is affected, but it can occur in both feet simultaneously.
Diagnosis
Your GP or podiatrist (a healthcare professional who specialises in foot care) may be able to diagnose the cause of your heel pain by asking about your symptoms and examining your heel and foot. You will usually only need further tests if you have additional symptoms that suggest the cause of your heel pain is not inflammation, such as numbness or a tingling sensation in your foot, this could be a sign of nerve damage in your feet and legs (peripheral neuropathy) your foot feels hot and you have a high temperature (fever) of 38C (100.4F) or above - these could be signs of a bone infection, you have stiffness and swelling in your heel, this could be a sign of arthritis. Possible further tests may include blood tests, X-rays - where small doses of radiation are used to detect problems with your bones and tissues, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound scan, which are more detailed scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
Plantar fasciitis is usually controlled with conservative treatment. Following control of the pain and inflammation an orthotic (a custom made shoe insert) will be used to stabilize your foot and prevent a recurrence. Over 98% of the time heel spurs and plantar fasciitis can be controlled by this treatment and surgery can be avoided. The orthotic prevents excess pronation and prevents lengthening of the plantar fascia and continued tearing of the fascia. Usually a slight heel lift and a firm shank in the shoe will also help to reduce the severity of this problem. The office visit will be used for careful examination and review to distinguish plantar fasciitis and plantar heel pain syndrome from other problems, many of which are outlined below. It is important to distinguish between a stress reaction of the calcaneus and plantar fasciitis. A feature of many calcaneal stress fractures is pain on lateral and medial compression of the calcaneus.

Surgical Treatment
In cases that do not respond to any conservative treatment, surgical release of the plantar fascia may be considered. Plantar fasciotomy may be performed using open, endoscopic or radiofrequency lesioning techniques. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with plantar fasciitis. Potential risk factors include flattening of the longitudinal arch and heel hypoesthesia as well as the potential complications associated with rupture of the plantar fascia and complications related to anesthesia.
What May Cause Heel Pain To Appear

Overview
The plantar fascia is made up of 3 distinct parts: the medial, central, and lateral bands. The central plantar fascia is the thickest and strongest section, and this segment is also the most likely to be involved with plantar fasciitis. In normal circumstances, the plantar fascia acts like a windlass mechanism to provide tension and support through the arch. It functions as a tension bridge in the foot, providing both static support and dynamic shock absorption.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis symptoms are usually exacerbated via "traction" (or stretching) forces on the plantar fascia. In simple terms, you plantar fascia is repeatedly overstretched. The most common reason for the overstretching are an elongated arch due to either poor foot biomechanics (eg overpronation) or weakness of your foot arch muscles. Compression type plantar fascia injuries have a traumatic history. Landing on a sharp object that bruises your plantar fascia is your most likely truma. The location of plantar fasciitis pain will be further under your arch than under your heel, which is more likely to be a fat pad contusion if a single trauma caused your pain. The compression type plantar fasciitis can confused with a fat pad contusion that is often described as a "stone bruise".
Symptoms
The condition typically starts gradually with mild pain at the heel bone often referred to as a stone bruise. You're more likely to feel it after (not during) exercise. The pain classically occurs right after getting up in the morning and after a period of sitting. If you don't treat plantar fasciitis, it may become a chronic condition. You may not be able to keep up your level of activity, and you may develop symptoms of foot, knee, hip and back problems because plantar fasciitis can change the way you walk.
Diagnosis
During the physical exam, your doctor checks for points of tenderness in your foot. The location of your pain can help determine its cause. Usually no tests are necessary. The diagnosis is made based on the history and physical examination. Occasionally your doctor may suggest an X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to make sure your pain isn't being caused by another problem, such as a stress fracture or a pinched nerve. Sometimes an X-ray shows a spur of bone projecting forward from the heel bone. In the past, these bone spurs were often blamed for heel pain and removed surgically. But many people who have bone spurs on their heels have no heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
No single treatment works best for everyone with plantar fasciitis. But there are many things you can try to help your foot get better. Give your feet a rest. Cut back on activities that make your foot hurt. Try not to walk or run on hard surfaces. To reduce pain and swelling, try putting ice on your heel. Or take an over-the-counter pain reliever like ibuprofen (such as Advil or Motrin) or naproxen (such as Aleve). Do toe stretches camera.gif, calf stretches camera.gif and towel stretches camera.gif several times a day, especially when you first get up in the morning. (For towel stretches, you pull on both ends of a rolled towel that you place under the ball of your foot.) Get a new pair of shoes. Pick shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole. Or try heel cups or shoe inserts. Use them in both shoes, even if only one foot hurts. If these treatments do not help, your doctor may recommend splints that you wear at night, shots of medicine (such as a steroid) in your heel, or other treatments. You probably will not need surgery. Doctors only suggest it for people who still have pain after trying other treatments for 6 to 12 months. Plantar fasciitis most often occurs because of injuries that have happened over time. With treatment, you will have less pain within a few weeks. But it may take time for the pain to go away completely. It may take a few months to a year. Stay with your treatment. If you don't, you may have constant pain when you stand or walk. The sooner you start treatment, the sooner your feet will stop hurting.

Surgical Treatment
More invasive procedures to treat plantar fasciitis are usually sought only after other treatment has failed to produce favorable results. Corticosteroid injections deliver medicine into the injured fascia to reduce pain. However, this treatment may weaken the plantar fascia and result in further damage. In addition, extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is a treatment where sound waves are sent through the damaged tissue in order to stimulate the damaged tissue and encourage healing. This method is relatively new in treating plantar fasciitis and your doctor will be able to tell you if it is the right method for you. Lastly, surgery is the last option for those suffering from chronic or severe plantar fasciitis.
Stretching Exercises
In one exercise, you lean forward against a wall with one knee straight and heel on the ground. Your other knee is bent. Your heel cord and foot arch stretch as you lean. Hold for 10 seconds, relax and straighten up. Repeat 20 times for each sore heel. It is important to keep the knee fully extended on the side being stretched. In another exercise, you lean forward onto a countertop, spreading your feet apart with one foot in front of the other. Flex your knees and squat down, keeping your heels on the ground as long as possible. Your heel cords and foot arches will stretch as the heels come up in the stretch. Hold for 10 seconds, relax and straighten up. Repeat 20 times. About 90 percent of people with plantar fasciitis improve significantly after two months of initial treatment. You may be advised to use shoes with shock-absorbing soles or fitted with an off-the-shelf shoe insert device like a rubber heel pad. Your foot may be taped into a specific position. If your plantar fasciitis continues after a few months of conservative treatment, your doctor may inject your heel with steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. If you still have symptoms, you may need to wear a walking cast for two to three weeks or a positional splint when you sleep. In a few cases, surgery is needed for chronically contracted tissue.