Living With Achilles Tendinitis
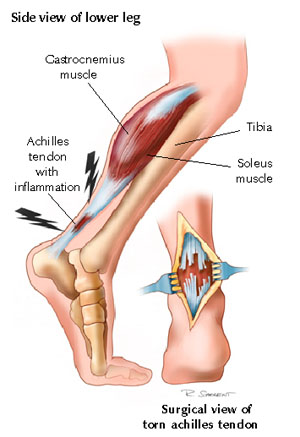
 Achilles tendinitis (tendonitis) or Achilles tendon inflammation occurs when the Achilles tendon becomes inflamed, as a result, of the Achilles tendon being put under too much strain. The Achilles tendon joins the calf muscles to the heel bone, and is found at the back of a person's lower leg. It is the largest tendon in the body and can endure great force, but is still susceptible to injury. Achilles tendinitis is usually the result of strenuous, high impact exercise, such as running. If ignored, Achilles tendinitis can lead to the tendon tearing or rupturing, and therefore it is important to seek the necessary treatment. Sometimes, treatment can be as simple as getting rest or changing an exercise routine. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be required.
Achilles tendinitis (tendonitis) or Achilles tendon inflammation occurs when the Achilles tendon becomes inflamed, as a result, of the Achilles tendon being put under too much strain. The Achilles tendon joins the calf muscles to the heel bone, and is found at the back of a person's lower leg. It is the largest tendon in the body and can endure great force, but is still susceptible to injury. Achilles tendinitis is usually the result of strenuous, high impact exercise, such as running. If ignored, Achilles tendinitis can lead to the tendon tearing or rupturing, and therefore it is important to seek the necessary treatment. Sometimes, treatment can be as simple as getting rest or changing an exercise routine. However, in more severe cases, surgery may be required.
Causes
Achilles tendonitis most commonly occurs due to repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on the Achilles tendon. This typically occurs due to excessive walking, running or jumping activities. Occasionally, it may occur suddenly due to a high force going through the Achilles tendon beyond what it can withstand. This may be due to a sudden acceleration or forceful jump. The condition may also occur following a calf or Achilles tear, following a poorly rehabilitated sprained ankle or in patients with poor foot biomechanics or inappropriate footwear. In athletes, this condition is commonly seen in running sports such as marathon, triathlon, football and athletics.
Symptoms
Mild ache in the back of the lower leg, especially after running. More acute pain may occur after prolonged activity, Tenderness or stiffness in the morning. In most cases the pain associated with Achilles tendinitis is more annoying than debilitating, making sufferers regret activity after the fact, but not keeping them from doing it. More severe pain around the Achilles tendon may be a symptom of a much more serious ruptured tendon.
Diagnosis
During an examination of the foot and ankle, you doctor will look for the following signs, Achilles tendon swelling or thickening. Bone spurs appearing at the lower part of the tendon at the back of the hell. Pain at the middle or lower area of the Achilles tendon. Limited range of motion of the foot and ankle, and a decreased ability to flex the foot. Your doctor may perform imaging tests, such as X-rays and MRI scans, to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendinitis. X-rays show images of the bones and can help the physician to determine if the Achilles tendon has become hardened, which indicated insertional Achilles tendinitis. MRI scans may not be necessary, but they are important guides if you are recommended to have surgical treatment. An MRI can show the severity of the damage and determine what kind of procedure would be best to address the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Supportive shoes and orthotics. Pain from insertional Achilles tendinitis is often helped by certain shoes, as well as orthotic devices. For example, shoes that are softer at the back of the heel can reduce irritation of the tendon. In addition, heel lifts can take some strain off the tendon. Heel lifts are also very helpful for patients with insertional tendinitis because they can move the heel away from the back of the shoe, where rubbing can occur. They also take some strain off the tendon. Like a heel lift, a silicone Achilles sleeve can reduce irritation from the back of a shoe. If your pain is severe, your doctor may recommend a walking boot for a short time. This gives the tendon a chance to rest before any therapy is begun. Extended use of a boot is discouraged, though, because it can weaken your calf muscle. Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT). During this procedure, high-energy shockwave impulses stimulate the healing process in damaged tendon tissue. ESWT has not shown consistent results and, therefore, is not commonly performed. ESWT is noninvasive-it does not require a surgical incision. Because of the minimal risk involved, ESWT is sometimes tried before surgery is considered.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery should be considered to relieve Achilles tendinitis only if the pain does not improve after 6 months of nonsurgical treatment. The specific type of surgery depends on the location of the tendinitis and the amount of damage to the tendon. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the Achilles tendon, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite consistent stretching. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope-an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Gastrocnemius recession can be performed with or without d?bridement, which is removal of damaged tissue. D?bridement and repair (tendon has less than 50% damage). The goal of this operation is to remove the damaged part of the Achilles tendon. Once the unhealthy portion of the tendon has been removed, the remaining tendon is repaired with sutures, or stitches to complete the repair. In insertional tendinitis, the bone spur is also removed. Repair of the tendon in these instances may require the use of metal or plastic anchors to help hold the Achilles tendon to the heel bone, where it attaches. After d?bridement and repair, most patients are allowed to walk in a removable boot or cast within 2 weeks, although this period depends upon the amount of damage to the tendon. D?bridement with tendon transfer (tendon has greater than 50% damage). In cases where more than 50% of the Achilles tendon is not healthy and requires removal, the remaining portion of the tendon is not strong enough to function alone. To prevent the remaining tendon from rupturing with activity, an Achilles tendon transfer is performed. The tendon that helps the big toe point down is moved to the heel bone to add strength to the damaged tendon. Although this sounds severe, the big toe will still be able to move, and most patients will not notice a change in the way they walk or run. Depending on the extent of damage to the tendon, some patients may not be able to return to competitive sports or running. Recovery. Most patients have good results from surgery. The main factor in surgical recovery is the amount of damage to the tendon. The greater the amount of tendon involved, the longer the recovery period, and the less likely a patient will be able to return to sports activity. Physical therapy is an important part of recovery. Many patients require 12 months of rehabilitation before they are pain-free.
Prevention
Stay in good shape year-round and try to keep your muscles as strong as they can be. Strong, flexible muscles work more efficiently and put less stress on your tendon. Increase the intensity and length of your exercise sessions gradually. This is especially important if you've been inactive for a while or you're new to a sport. Always warm up before you go for a run or play a sport. If your muscles are tight, your Achilles tendons have to work harder to compensate. Stretch it out. Stretch your legs, especially your calves, hamstrings, quadriceps, and thigh muscles - these muscles help stabilize your knee while running. Get shoes that fit properly and are designed for your sport. If you're a jogger, go to a running specialty store and have a trained professional help you select shoes that match your foot type and offer plenty of support. Replace your shoes before they become worn out. Try to run on softer surfaces like grass, dirt trails, or synthetic tracks. Hard surfaces like concrete or asphalt can put extra pressure on the joints. Also avoid running up or down hills as much as possible. Vary your exercise routine. Work different muscle groups to keep yourself in good overall shape and keep individual muscles from getting overused. If you notice any symptoms of Achilles tendonitis, stop running or doing activities that put stress on your feet. Wait until all the pain is gone or you have been cleared to start participating again by a doctor.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis And Simple Methods To Prevent It
Overview
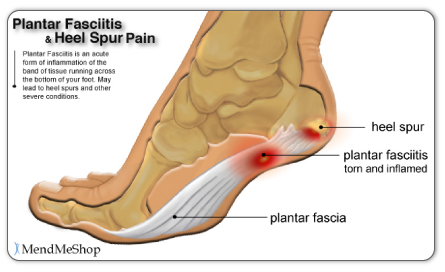
The plantar fascia is a strong, relatively inflexible, fibrous ligament band that runs through the bottom of the foot. That band helps to keep the complex arch system of the foot, absorb shock, plays a role in body balance and in the various phases of gait. The band transmits your weight across the bottom of the foot with each step you take. When the heel of the trailing leg starts to get off the ground, the band bears tension that is approximately twice the body weight. The tension on the band at this moment is even greater if the calf muscles are not flexible enough.
Causes
It usually starts following an increase in activity levels. Increase in weight. Standing for long periods. Poor footwear. Tight muscle groups. Abnormal pressure on the plantar Fascia can be caused by any of the above. The plantar fascia becomes inflamed and tiny rips can occur where it attaches into the inside of the heel bone. The area becomes inflamed and swollen, and it is the increase in fluid to the area that accumulates when weight is taken off the area that then causes the pain on standing.
Symptoms
Plantar fasciitis commonly causes a stabbing pain in the heel of the foot, which is worse during the first few steps of the day after awakening. As you continue to walk on the affected foot, the pain gradually lessens. Usually, only one foot is affected, but it can occur in both feet simultaneously.
Diagnosis
Your GP or podiatrist (a healthcare professional who specialises in foot care) may be able to diagnose the cause of your heel pain by asking about your symptoms and examining your heel and foot. You will usually only need further tests if you have additional symptoms that suggest the cause of your heel pain is not inflammation, such as numbness or a tingling sensation in your foot, this could be a sign of nerve damage in your feet and legs (peripheral neuropathy) your foot feels hot and you have a high temperature (fever) of 38C (100.4F) or above - these could be signs of a bone infection, you have stiffness and swelling in your heel, this could be a sign of arthritis. Possible further tests may include blood tests, X-rays - where small doses of radiation are used to detect problems with your bones and tissues, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound scan, which are more detailed scans.
Non Surgical Treatment
Plantar fasciitis is usually controlled with conservative treatment. Following control of the pain and inflammation an orthotic (a custom made shoe insert) will be used to stabilize your foot and prevent a recurrence. Over 98% of the time heel spurs and plantar fasciitis can be controlled by this treatment and surgery can be avoided. The orthotic prevents excess pronation and prevents lengthening of the plantar fascia and continued tearing of the fascia. Usually a slight heel lift and a firm shank in the shoe will also help to reduce the severity of this problem. The office visit will be used for careful examination and review to distinguish plantar fasciitis and plantar heel pain syndrome from other problems, many of which are outlined below. It is important to distinguish between a stress reaction of the calcaneus and plantar fasciitis. A feature of many calcaneal stress fractures is pain on lateral and medial compression of the calcaneus.

Surgical Treatment
In cases that do not respond to any conservative treatment, surgical release of the plantar fascia may be considered. Plantar fasciotomy may be performed using open, endoscopic or radiofrequency lesioning techniques. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with plantar fasciitis. Potential risk factors include flattening of the longitudinal arch and heel hypoesthesia as well as the potential complications associated with rupture of the plantar fascia and complications related to anesthesia.
What May Cause Heel Pain To Appear

Overview
The plantar fascia is made up of 3 distinct parts: the medial, central, and lateral bands. The central plantar fascia is the thickest and strongest section, and this segment is also the most likely to be involved with plantar fasciitis. In normal circumstances, the plantar fascia acts like a windlass mechanism to provide tension and support through the arch. It functions as a tension bridge in the foot, providing both static support and dynamic shock absorption.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis symptoms are usually exacerbated via "traction" (or stretching) forces on the plantar fascia. In simple terms, you plantar fascia is repeatedly overstretched. The most common reason for the overstretching are an elongated arch due to either poor foot biomechanics (eg overpronation) or weakness of your foot arch muscles. Compression type plantar fascia injuries have a traumatic history. Landing on a sharp object that bruises your plantar fascia is your most likely truma. The location of plantar fasciitis pain will be further under your arch than under your heel, which is more likely to be a fat pad contusion if a single trauma caused your pain. The compression type plantar fasciitis can confused with a fat pad contusion that is often described as a "stone bruise".
Symptoms
The condition typically starts gradually with mild pain at the heel bone often referred to as a stone bruise. You're more likely to feel it after (not during) exercise. The pain classically occurs right after getting up in the morning and after a period of sitting. If you don't treat plantar fasciitis, it may become a chronic condition. You may not be able to keep up your level of activity, and you may develop symptoms of foot, knee, hip and back problems because plantar fasciitis can change the way you walk.
Diagnosis
During the physical exam, your doctor checks for points of tenderness in your foot. The location of your pain can help determine its cause. Usually no tests are necessary. The diagnosis is made based on the history and physical examination. Occasionally your doctor may suggest an X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to make sure your pain isn't being caused by another problem, such as a stress fracture or a pinched nerve. Sometimes an X-ray shows a spur of bone projecting forward from the heel bone. In the past, these bone spurs were often blamed for heel pain and removed surgically. But many people who have bone spurs on their heels have no heel pain.
Non Surgical Treatment
No single treatment works best for everyone with plantar fasciitis. But there are many things you can try to help your foot get better. Give your feet a rest. Cut back on activities that make your foot hurt. Try not to walk or run on hard surfaces. To reduce pain and swelling, try putting ice on your heel. Or take an over-the-counter pain reliever like ibuprofen (such as Advil or Motrin) or naproxen (such as Aleve). Do toe stretches camera.gif, calf stretches camera.gif and towel stretches camera.gif several times a day, especially when you first get up in the morning. (For towel stretches, you pull on both ends of a rolled towel that you place under the ball of your foot.) Get a new pair of shoes. Pick shoes with good arch support and a cushioned sole. Or try heel cups or shoe inserts. Use them in both shoes, even if only one foot hurts. If these treatments do not help, your doctor may recommend splints that you wear at night, shots of medicine (such as a steroid) in your heel, or other treatments. You probably will not need surgery. Doctors only suggest it for people who still have pain after trying other treatments for 6 to 12 months. Plantar fasciitis most often occurs because of injuries that have happened over time. With treatment, you will have less pain within a few weeks. But it may take time for the pain to go away completely. It may take a few months to a year. Stay with your treatment. If you don't, you may have constant pain when you stand or walk. The sooner you start treatment, the sooner your feet will stop hurting.

Surgical Treatment
More invasive procedures to treat plantar fasciitis are usually sought only after other treatment has failed to produce favorable results. Corticosteroid injections deliver medicine into the injured fascia to reduce pain. However, this treatment may weaken the plantar fascia and result in further damage. In addition, extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is a treatment where sound waves are sent through the damaged tissue in order to stimulate the damaged tissue and encourage healing. This method is relatively new in treating plantar fasciitis and your doctor will be able to tell you if it is the right method for you. Lastly, surgery is the last option for those suffering from chronic or severe plantar fasciitis.
Stretching Exercises
In one exercise, you lean forward against a wall with one knee straight and heel on the ground. Your other knee is bent. Your heel cord and foot arch stretch as you lean. Hold for 10 seconds, relax and straighten up. Repeat 20 times for each sore heel. It is important to keep the knee fully extended on the side being stretched. In another exercise, you lean forward onto a countertop, spreading your feet apart with one foot in front of the other. Flex your knees and squat down, keeping your heels on the ground as long as possible. Your heel cords and foot arches will stretch as the heels come up in the stretch. Hold for 10 seconds, relax and straighten up. Repeat 20 times. About 90 percent of people with plantar fasciitis improve significantly after two months of initial treatment. You may be advised to use shoes with shock-absorbing soles or fitted with an off-the-shelf shoe insert device like a rubber heel pad. Your foot may be taped into a specific position. If your plantar fasciitis continues after a few months of conservative treatment, your doctor may inject your heel with steroidal anti-inflammatory medication. If you still have symptoms, you may need to wear a walking cast for two to three weeks or a positional splint when you sleep. In a few cases, surgery is needed for chronically contracted tissue.
What Will Cause Pain Under The Heel And Ways To Eliminate It
Overview
There are many diagnoses within the differential of heel pain; however, plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain for which professional care is sought. Approximately 10% of the United States population experiences bouts of heel pain, which results in 1 million visits per year to medical professionals for treatment of plantar fasciitis. The annual cost of treatments for plantar fasciitis is estimated to be between $192 and $376 million dollars. The etiology of this condition is multifactorial, and the condition can occur traumatically; however, most cases are from overuse stresses.
Causes
Plantar fasciitis is a painful disorder in the lower part of your foot usually around the heel. That pain usually hurts as you get up in the morning when you try to stand on your feet, or after any periods of inactivity. It is a disorder of a tough and strong band that connects the heel bone to the toes. Plantar Fasciitis is caused by injuring that tough band on the bottom of the foot. The following may be the causes of plantar fasciitis. Tight calf muscles or tight Achilles tendon produces repetitive over-stretching of the plantar fascia. Gait and balance Problem may be a dominant cause of this disorder. Many people have a special style of walking, with something unique that causes some kind of imbalance in their body. It might be something like locked knees, feet that turn-out, a weak abdomen etc. This imbalance may place some pressure on the fascia, which eventually causes plantar fasciitis. Weak foot muscles don’t give enough support to the plantar fascia. The small muscles in the foot give the foot its shape by keeping the bones in place and by expanding and contracting to make a movement. Weak foot muscles will allow greater stress on the fascia. Foot anatomical problems such as flat feet or high arches can make the fascia ligament work or stretch abnormally. Flattening of the fat pad at the sole of the feet under the heels is a Degeneration process that is caused by poor footwear or by age. Shoes that have no proper heel cup can flatten that fat pad quite quickly and cause this disorder. Walking in shoes which do not have good arch support is considered to be a cause of plantar fasciitis. Wearing inadequate or worn out shoes may place more stress on the fascia ligament. If you wear shoes that don't fit you by size or width, you may put your feet under excessive stress. Overweight Men and women are more vulnerable to developing the condition because of the excess weight on the foot. Pregnant women are at risk due to gaining weight through pregnancy and due to the pregnancy hormones that make ligaments loosen and relax. Sudden increase of activity like starting to run long distance or complete change of daily activity can cause heel pain and this disorder. Practice of repetitive athletic activities, like long distance running, playing a ball game, dancing or jumping, is a common cause for the disorder. Actually it is considered as one of the most common running injuries. Spending long periods of time on your feet everyday can cause plantar fasciitis. Working on your feet a few hours a day evey day may be the reason for your heel pain.
Symptoms
A sharp pain in the center of your heel will most likely be one of the biggest symptoms of plantar fasciitis. A classic sign of plantar fasciitis is when the pain is worst during the first steps you take in the morning.
Diagnosis
A physical exam performed in the office along with the diagnostic studies as an x-ray. An MRI may also be required to rule out a stress fracture, or a tear of the plantar fascia. These are conditions that do not normally respond to common plantar fasciitis treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment for heel pain usually involves using a combination of techniques, such as stretches and painkillers, to relieve pain and speed up recovery. Most cases of heel pain get better within 12 months. Surgery may be recommended as a last resort if your symptoms don't improve after this time. Only 1 in 20 people with heel pain will need surgery. Whenever possible, rest the affected foot by not walking long distances and standing for long periods. However, you should regularly stretch your feet and calves using exercises such as those described below. Pain relief. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can be used to help relieve pain. Some people also find applying an ice pack to the affected heel for 5-10 minutes can help relieve pain and inflammation. However, do not apply an ice pack directly to your skin. Instead, wrap it in a towel. If you do not have an ice pack, you can use a packet of frozen vegetables.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery for plantar fasciitis can be very successful in the right patients. While there are potential complications, about 70-80% of patients will find relief after plantar fascia release surgery. This may not be perfect, but if plantar fasciitis has been slowing you down for a year or more, it may well be worth these potential risks of surgery. New surgical techniques allow surgery to release the plantar fascia to be performed through small incisions using a tiny camera to locate and cut the plantar fascia. This procedure is called an endoscopic plantar fascia release. Some surgeons are concerned that the endoscopic plantar fascia release procedure increases the risk of damage to the small nerves of the foot. While there is no definitive answer that this endoscopic plantar fascia release is better or worse than a traditional plantar fascia release, most surgeons still prefer the traditional approach.
What Causes Heel Pain

Overview
The Plantar Fascia is a strong ligament-like structure under the arch of the foot that runs from the heel bone to the ball of the foot. If we could see it in isolation it has a triangular shape when looked at from underneath but has a curved shape when looked at from the side - much like a sail boat’s sail billowing in the wind. The most functional piece is from the front-bottom-inside area of the heel bone (calcaneous) to the joint of the big toe (hallux) and this is where the majority of stress of walking (and running and jumping) is taken by the fascia. How your plantar fascia reacts to and recovers from this stress is what determines the extent and nature of your plantar fasciitis.
Causes
The cause of plantar fasciitis is often unclear and may be multifactorial. Because of the high incidence in runners, it is best postulated to be caused by repetitive microtrauma. Possible risk factors include obesity, occupations requiring prolonged standing and weight-bearing, and heel spurs. Other risk factors may be broadly classified as either extrinsic (training errors and equipment) or intrinsic (functional, structural, or degenerative). Training errors are among the major causes of plantar fasciitis. Athletes usually have a history of an increase in distance, intensity, or duration of activity. The addition of speed workouts, plyometrics, and hill workouts are particularly high-risk behaviors for the development of plantar fasciitis. Running indoors on poorly cushioned surfaces is also a risk factor. Appropriate equipment is important. Athletes and others who spend prolonged time on their feet should wear an appropriate shoe type for their foot type and activity. Athletic shoes rapidly lose cushioning properties. Athletes who use shoe-sole repair materials are especially at risk if they do not change shoes often. Athletes who train in lightweight and minimally cushioned shoes (instead of heavier training flats) are also at higher risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Among the symptoms for Plantar Fasciitis is pain usually felt on the underside of the heel, often most intense with the first steps after getting out of bed in the morning. It is commonly associated with long periods of weight bearing or sudden changes in weight bearing or activity. Plantar Fasciitis also called “policeman’s heel” is presented by a sharp stabbing pain at the bottom or front of the heel bone. In most cases, heel pain is more severe following periods of inactivity when getting up and then subsides, turning into a dull ache.
Diagnosis
Plantar fasciitis is usually diagnosed by your physiotherapist or sports doctor based on your symptoms, history and clinical examination. After confirming your plantar fasciitis they will investigate WHY you are likely to be predisposed to plantar fasciitis and develop a treatment plan to decrease your chance of future bouts. X-rays may show calcification within the plantar fascia or at its insertion into the calcaneus, which is known as a calcaneal or heel spur. Ultrasound scans and MRI are used to identify any plantar fasciitis tears, inflammation or calcification. Pathology tests (including screening for HLA B27 antigen) may identify spondyloarthritis, which can cause symptoms similar to plantar fasciitis.
Non Surgical Treatment
Most health care providers agree that initial treatment for plantar fasciitis should be quite conservative. You'll probably be advised to avoid any exercise that is making your pain worse. Your doctor may also advise one or more of these treatment options. A heel pad. In plantar fasciitis, a heel pad is sometimes used to cushion the painful heel if you spend a great deal of time on your feet on hard surfaces. Also, over-the-counter or custom-made orthotics, which fit inside your shoes, may be constructed to address specific imbalances you may have with foot placement or gait. Stretching: Stretching exercises performed three to five times a day can help elongate the heel cord. Ice: You may be advised to apply ice packs to your heel or to use an ice block to massage the plantar fascia before going to bed each night. Pain relievers: Simple over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, are often helpful in decreasing inflammation and pain. If you have stomach trouble from such drugs, your health care provider may prescribe an alternative. A night splint: A night splint is sometimes used to hold your foot at a specific angle, which prevents the plantar fascia from shortening during sleep. Ultrasound: Ultrasound therapy can be performed to decrease inflammation and aid healing. Steroid injections: Anti-inflammatory steroid injections directly into the tissue around your heel may be temporarily helpful. However, if these injections are used too many times, you may suffer other complications, such as shrinking of the fat pad of your heel, which you need for insulation. Loss of the fat pad could actually increase your pain, or could even rupture the plantar fascia in rare cases. Walking cast: In cases of long-term plantar fasciitis unresponsive to usual treatments, your doctor may recommend that you wear a short walking cast for about three weeks. This ensures that your foot is held in a position that allows the plantar fascia to heal in a stretched, rather than shortened, position. Shock wave therapy, Extracorporeal shock wave therapy which may be prescribed prior to considering surgery if your symptoms have persisted for more than six months. This treatment does not involve any actual incisions being made rather it uses a high intensity shock wave to stimulate healing of the plantar fascia.

Surgical Treatment
When more conservative methods have failed to reduce plantar fasciitis pain, your doctor may suggest extracorporeal shock wave therapy, which is used to treat chronic plantar fasciitis. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy uses sound waves to stimulate healing, but may cause bruises, numbness, tingling, swelling, and pain. When all else fails, surgery may be recommended to detach the plantar fascia from the heel bone. Few people need surgery to treat the condition.
Symptoms Of Ingrown Toenail
TOE CONDITIONS: Ingrown toenails, blood accumulation under the nail plate (subungual hematoma), corns and calluses are all often seen as a result of playing baseball. It is important that good foot hygiene be practiced with washing between the toes and drying the feet well after bathing. Topical antifungals work well to treat athletes foot. ORTHOPEDIC INJURIES: Most orthopedic baseball foot and ankle injuries are acute or sudden. If an individuals foot or ankle is injured, seek immediate evaluation with one of our doctors. If your athlete has a baseball related injury, call our specialists at Advanced Foot and Ankle Center in McKinney and Prosper Texas at 972-542-2155. However, toe numbness and pain occurring together is one such problem that you cannot afford to ignore. Common symptoms are flat feet knee problems , burning sensation, numbness.
If you see just a thin line connecting the ball of your foot to your heel, you have high arches. If you have flat feet or high arches, you're more likely to get plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of your foot. Without proper arch support, you can have pain in your heels, arch, and leg. You can also develop bunions and hammertoes, which can become painful,” says Marlene Reid, a podiatrist, or foot and ankle doctor, in Naperville, IL. Shoes with good arch support and a slightly raised heel can help ward off trouble. Laces, buckles, or straps are best for high arches. See a foot doctor to get fitted with custom inserts for your shoes. Good running shoes, for example, can prevent heel pain, stress fractures , and other foot problems that can be brought on by running. A 2-inch heel is less damaging than a 4-inch heel. If you have flat feet, opt for chunky heels instead of skinny ones, Reid says.

Another solution is to wear custom foot orthotics, like ezWalker ® Performance Custom Orthotics, in your shoes to help correct your body posture, stabilize your balance, relieve pain during follow-through and evenly redistribute your weight on your feet. EzWalker® Custom Orthotics are specifically made for each of your feet to properly support your arches while reducing pressure on the balls of your feet. With ezWalker® Custom Orthotics, you'll walk from lateral heel to medial forefoot for better biomechanics of your entire body. This condition manifests as a skin lesion that assumes a ring-like pattern. It can affect any region of the body, right from the scalp to the foot. One such common home remedy is the use of bleach. Many people claim that this is a very effective ringworm treatment.

Went to Podiatrist after receiving pain pills to move, got MRI and he told me I have severe tear in plantor faciitis tendon. Have swelling or what I call a fatty feeling, as I have always had on ball of foot below left most two toes. And it seems to feel a little more fatty since I walked for the first time today after putting on a good pair of ankle boots. Any idea what the fatty feeling is on ball of foot. Lastly, I took the boot off at my stairs into my house 2 days ago and took a step using ball of left foot and it did not pop.
Cure Plantar Fasciitis And Foot Pain
knocked out the other one. The succeeding rounds also scored direct hits. Yet none of the tankers was killed though several were hard hit. One man had his right leg blown off and his left badly mangled. Private John J. Garry, an infantryman, moved over to the ditch to help the wounded tankers and was hit in the shoulder by a shell fragment. Medscape Reference features 129 medical calculators covering formulas, scales, and classifications. Plus, more than 600 drug monographs in our drug reference include integrated dosing calculators. Image Collections Bunions and hammer toes are progressive deformities. This means they get worse as time goes on. Shoe selection is only one causative factor, and sometimes does not cause these deformities at all. A 12 year old female patient with bunions certainly can't blame her shoes. Other risk factors like walking activity, heredity, and walking surface affect the rate and type of development of these deformities. Often hammertoes and bunions will be visible for many years before they become painful. Sometimes a change in activity, shoes, or weight gain can make a bunion or hammertoe seem suddenly very painful. The optimal excess weight gainer will probably include a mixture of diverse components in the right rates to make sure greatest healing and growth. It requires to add a top adequate nutrient degree to supply strength with regard to teaching as well as defeating an easy fat burning capacity which may restriction nutrition pertaining to development. Mammoth healthy proteins consists of nearly One thousand energy in a very full Four details offering and that is ample for probably the most tenacious hard-gainer (an individual which detects that it is hard to add lean muscle) to discover frequent gains for the machines and the actual hand mirror. Hammertoes may have several causes, but most commonly come about due to muscle imbalances. The tendons pulling the toe inward may be stronger than the ones that pull the toe straight, thus resulting in a toe that's bumped up in the middle. Hammertoes (or a tendency to develop them) might have been something you inherited from your parents (or grandparents, or third cousins), although they may also be caused or exacerbated by wearing shoes that scrunch the toes up into a small space (i.e. shoes with tiny little toe boxes and/or high heels—the usual lineup of suspects).  This kind of scrumptious proteins tremble style excellent which is set with vitamins and minerals with regard to packing on weight. With all the correct necessary protein powdered ingredients this particular proteins shake will give you 50g of additional health proteins along with large unhealthy calories which are not loaded with hammer toe syrup and also rubbish elements such as enhanced hammer toe flour. For getting final results, you'll be able to however try to eat your typical eating habits, nevertheless ingest 1-2 of these smoothies per day! Renal system legumes are rich in straightener which assists inside having much needed oxygen towards the cells. Pinto Pinto beans Health improvements If you don't have a health insurance plan, or you just don't feel like sitting for hours in a waiting room, you can treat the injury yourself. This article is not for the faint of heart, though. You will need to drill, hammer or otherwise insert a sharp object directly into your own fingernail or toenail! That's going to hurt, of course, but the pain will ease up right after you accomplish the task. For a more intimate and involved-in-the-moment picture, get down to the level of your subjects. Make sure your lens is at the same height as the children's eyes. Seeing a podiatrist is the way to go,” advises Wendy Vargas. That’s what she did when she had foot pain, and learned that she had a nerve problem that needed treatment. In addition to hammer toe, you might feel foot pain because of many other maladies. Plantar fasciitis, bunions, stress fractures, heel spurs, and several neural conditions can all cause foot pain. Most of these conditions are caused by footwear. Are the shoe choices you’re making going to cause you years and years of terrible pain? Hammer toes are the result of a tendon imbalancedue to foot mechanics or structure. Other causes include shoes, neuromusculardisorders, congenital disorders, and injury. The traditional technique to correct a hammertoe involves making an incision on the top of the toe and reaching the bones underneath. There are three bones in each lesser toe , and the surgeon directs his/her attention to the bone that is most prominently positioned on top. The tip of this bone is removed at the joint, which allows the toe to flatten down again. The surgeon then goes through a series of sequential tests to release or lengthen specific ligaments, tendons and soft tissue that act on the bones if the contracture is not fully relaxed when the bone is removed.
This kind of scrumptious proteins tremble style excellent which is set with vitamins and minerals with regard to packing on weight. With all the correct necessary protein powdered ingredients this particular proteins shake will give you 50g of additional health proteins along with large unhealthy calories which are not loaded with hammer toe syrup and also rubbish elements such as enhanced hammer toe flour. For getting final results, you'll be able to however try to eat your typical eating habits, nevertheless ingest 1-2 of these smoothies per day! Renal system legumes are rich in straightener which assists inside having much needed oxygen towards the cells. Pinto Pinto beans Health improvements If you don't have a health insurance plan, or you just don't feel like sitting for hours in a waiting room, you can treat the injury yourself. This article is not for the faint of heart, though. You will need to drill, hammer or otherwise insert a sharp object directly into your own fingernail or toenail! That's going to hurt, of course, but the pain will ease up right after you accomplish the task. For a more intimate and involved-in-the-moment picture, get down to the level of your subjects. Make sure your lens is at the same height as the children's eyes. Seeing a podiatrist is the way to go,” advises Wendy Vargas. That’s what she did when she had foot pain, and learned that she had a nerve problem that needed treatment. In addition to hammer toe, you might feel foot pain because of many other maladies. Plantar fasciitis, bunions, stress fractures, heel spurs, and several neural conditions can all cause foot pain. Most of these conditions are caused by footwear. Are the shoe choices you’re making going to cause you years and years of terrible pain? Hammer toes are the result of a tendon imbalancedue to foot mechanics or structure. Other causes include shoes, neuromusculardisorders, congenital disorders, and injury. The traditional technique to correct a hammertoe involves making an incision on the top of the toe and reaching the bones underneath. There are three bones in each lesser toe , and the surgeon directs his/her attention to the bone that is most prominently positioned on top. The tip of this bone is removed at the joint, which allows the toe to flatten down again. The surgeon then goes through a series of sequential tests to release or lengthen specific ligaments, tendons and soft tissue that act on the bones if the contracture is not fully relaxed when the bone is removed.